Four Companies Leading the Rise of Cybersecurity
Today, it is probably only a matter of time before a company faces a major cyber event. Software management company SolarWinds’ time came in December 2020. In what some describe as the largest cyberattack in US history, perpetrators introduced a vulnerability in the company’s Orion software that could potentially allow an attacker to compromise the server on which the software runs. The alarming part is that the attack hit key federal agencies and organisations, perhaps compromising national security. Early estimates are that roughly 250 organisations were affected.
Cyber threat events in the US and around the world are increasingly pervasive and sophisticated. The upward trajectory in the number of cyberattacks is expected to increase global security spending from approximately US$125 billion in 2020 to US$175 billion by 2024.1 Contributing to this growth is the accelerating migration to the cloud. Currently, only one-third of total workloads use cloud computing technology. As that number increases, more spending on cybersecurity will be needed to help prevent malicious attacks.2 Similarly, the rapid adoption of more internet-enabled devices also creates new targets for hackers who want to steal or ransom valuable data.
In this piece, we highlight four companies that are key players in the cybersecurity theme:
- CrowdStrike: A leading Endpoint Protection Platform
- Zscaler: A cloud-native platform offering Secure Web Gateways
- Okta: A key player in the Identity Access Management vertical
- Mimecast: A top provider of solutions that detect and block malicious emails
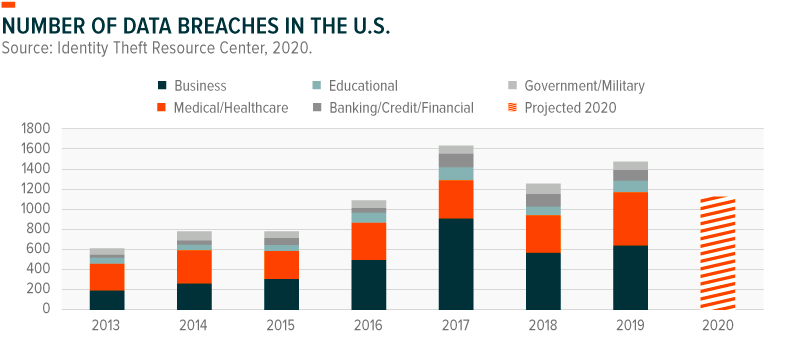
It is projected that over 380 million individuals had their data compromised in 20203
CrowdStrike: A Leading Endpoint Protection Platform
CrowdStrike is one of the leading cybersecurity companies in endpoint protection platforms (EPP), which helps customers to secure end-user devices such as mobile devices, laptops, and servers. CrowdStrike’s solution is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) that works continuously to detect and analyse threats. The solution is a 100% cloud-based architecture, which gives CrowdStrike a competitive advantage versus legacy, non-cloud incumbents. The company can set up its solution quickly and effectively in many different IT environments. For example, in the company’s Q4 fiscal year (FY) 2020, the company onboarded Target as a new client in just 10 days.
In the past, on-premises anti-virus software prevented cyberattacks by monitoring and scanning known threats in end-point files. But that security layer is largely reactive. Today’s best offerings leverage AI. CrowdStrike’s AI offering is called Threat Graph, the brains behind the company’s AI-enabled cybersecurity solutions. Threat Graph can help CrowdStrike handle 4 trillion cyber events per week and make 50 million decisions per minute.4 The data sets are processed in CrowdStrike’s cloud, creating a network effect where, the more data analysed across customers, the better Threat Graph AI-technology becomes.
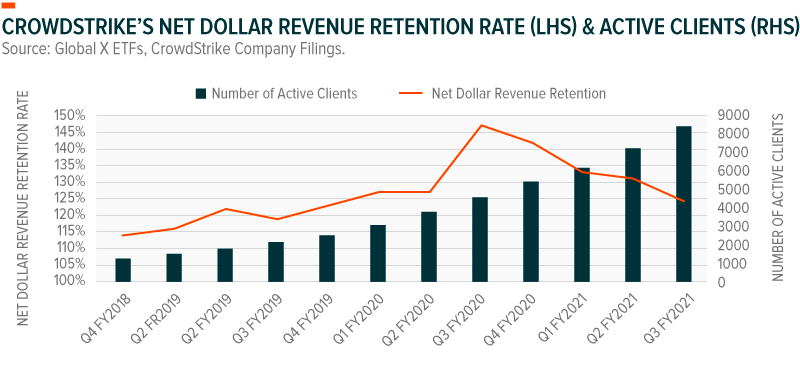
Cloud-based solutions can translate into robust recurring revenues. As of Q4 FY2020, CrowdStrike generated 92% of its total revenue from subscriptions.5 Also notable is that CrowdStrike has maintained a net dollar revenue retention rate higher than 120% since Q1 FY2019.6 A rate greater than 100% means that there is net growth from an existing customer base, either through price increases or upselling opportunities.
Zscaler: A Top Player in Secure Web Gateways
Zscaler is another 100% cloud-based cybersecurity platform, so there is no hardware to buy or manage, and the platform is always up to date. Zscaler makes 175,000 security cloud updates per day.7 Zscaler’s Secure Web Gateways (SGW) solutions primarily focus on giving customers secure access to internally managed applications, like corporate emails, through its Zscaler Private Access (ZPA). They also provide solutions for external applications, like customer relationship management (CRM) software, through Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA). A Secure Web Gateway prevents unsecured traffic from entering an internal network through external web applications. Zscaler is like a middleman, connecting users directly to applications without going through their network.
Zscaler offers capabilities that could eventually render the use of virtual private network (VPN) technologies obsolete. The company’s ZPA solution is easier to deploy, easier to manage, and more secure than traditional VPN solutions. ZPA provides users with access to internal apps, without the need to connect to a company’s network or expose those users to the internet. This architecture also completely limits the ability of a cyberattack to move horizontally across the network during a breach. The company describes this architecture as a Zero Trust Network, never extending the network to all users. Essentially, the network becomes deemphasised and the internet becomes the new corporate network.8
Securing access to internal and external apps on laptops, smartphones, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices is now a top priority for organisations, particularly with remote and hybrid work going mainstream. According to research firm Gartner, by 2023, 60% of enterprises will phase out most of their remote access VPNs in favor of Zero Trust Networks like Zscaler’s offering.9
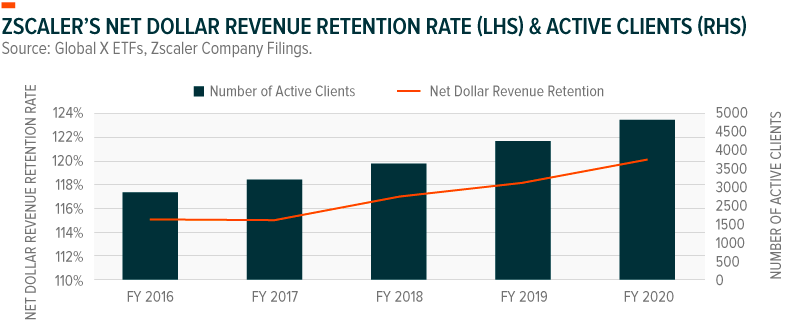
Zscaler’s net dollar revenue retention rate hit the 120% level as of the end of Fiscal Year 2020, indicating continued growth among its existing user base.10 Importantly, the company believes it has a 6x upsell opportunity with existing customers on ZIA and ZPA alone.11
Okta: A Fast-Growing Company in Identity Access Management
Okta is a leading cybersecurity company in the Identity Access Management (IAM) vertical. This vertical focuses on enabling the right individuals and employees to access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons.12 Multi-factor authentication (MFA), application programming interface (API) access management, and single sign-on (SSO) are a few identity solutions that companies increasingly leverage to ensure the right users are authorised to access different applications.
Companies in the IAM vertical are also expected to benefit from the shift towards remote and hybrid work environments. With employees working from multiple locations and connecting from different devices, IAM lets IT departments monitor who’s accessing specific apps at a given time. IAM also helps companies to monitor and secure points of access given to contractors or customers that must access certain internal applications.
From an end-user standpoint, Okta’s IAM solutions provide access to all applications within a single portal. This feature reduces login-related helpdesk calls by 50% and makes it 50% faster for users to log in and use new apps.13 Okta estimates the total addressable market for workforce identity is US$30 billion and the market for customer identity is $25 billion.14
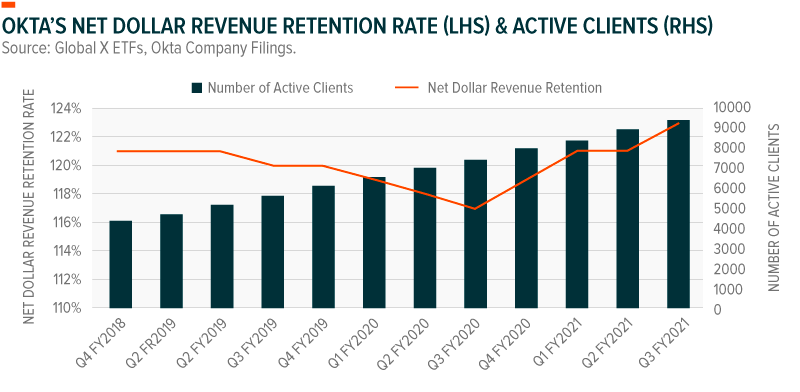
Like CrowdStrike and Zscaler, Okta’s solutions are cloud native. Ninety-four percent of the company’s revenue is recurring, as it’s generated from subscription services. Okta is another company with solid net dollar revenue retention figures, registering 123% for the trailing 12-month period in Q3 FY2021, a 2% increase from previous quarter.
Mimecast: A Top Provider in Email Security
Mimecast is a top player in probably the best-known type of cybersecurity vertical, Secure Email Gateways. Ninety-five percent of cyberattacks leverage email, making it the preferred channel for opportunistic and targeted attacks.15 Mimecast’s opportunity set is significant, with approximately 1 billion worldwide business email users.16 Today, the company has roughly 15 million users, or 1.5% penetration of the total global market.17
The goal of mass phishing and targeted spear-phishing attacks is to appeal to recipients with a message that resonates with them and coerces them into an action.18 Attackers want to steal money or critical data like intellectual property. Between October 2013 and May 2018, the FBI estimates that US$12 billion dollars were lost from email compromise.19 Email phishing and impersonation fraud are ever-present today, but the COVID-19 pandemic makes the environment ripe for even more such behaviours with people spending more time online. In fact, email phishing and impersonation fraud increased by 30% in the first 100 days of COVID-19 alone.20
Mimecast provides solutions that detect and block emails that include known or unknown malware, malicious URLs, and impersonation of senior staff members or third-party organisations like banks, federal agencies, or even customers and suppliers. Mimecast complements its traditional detection techniques with AI features such as deep learning to identify images and logos not safe for work, machine learning to detect anomalous risky patterns in emails, and supervised learning to categorise high risk links.
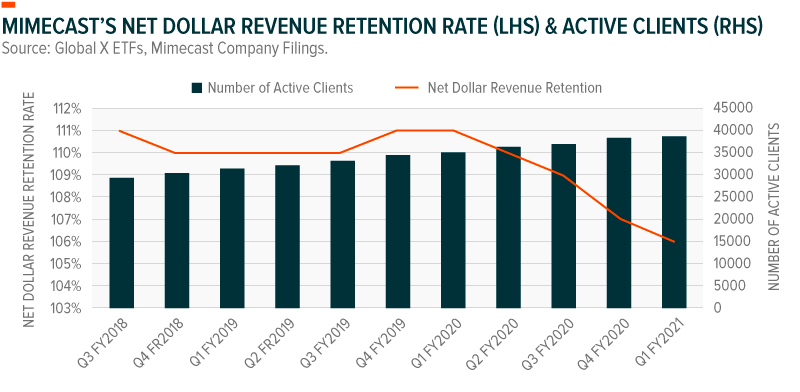
Mimecast also implements a cloud-native architecture, combining agility with an attractive business model. The company has sustained a net dollar revenue retention rate above 100% over the last few years, adding to the strength of cybersecurity companies’ business models.21
Conclusion
Cybersecurity not only grabs headlines these days, it also grabs budgets. The growing number of cyberattacks and their potential implications for sectors and governments worldwide makes cybersecurity tools indispensable for organisations to operate securely across multiple business functions. Whether it’s email, identity management, access to internal and external apps, or protecting end-user devices, the four companies highlighted here are key players in keeping this increasingly digital world safer and exemplify the multi-faceted nature of the cybersecurity industry.
This document is not intended to be, or does not constitute, investment research