Digital Economy Discovers a Potential Frontier for Growth Thanks to Generative AI
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3, the underlying technology behind OpenAI’s immensely popular ChatGPT, are smarter by several orders of magnitude than their predecessors. These technological leaps democratize access to automated decision making in an unprecedented fashion, marking a new chapter in the rise of applied artificial intelligence (AI). These models are faster, cheaper, and more accurate than previous AI systems, with the potential to spur a massive innovation cycle, boosting productivity and powering a whole new set of applications and tools.
As AI matures, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and digital media will receive strong boosts, allowing leading platforms in these arenas to solidify their positioning and compound the addressable market opportunities at their disposal.
Key Takeaways
- The new generation of large language models marks a paradigm shift in the capabilities and democratization of artificial intelligence.
- AI could boost productivity, save costs, and create new experiences for consumers, likely drawing a broad investment cycle in the larger technology space.
- There exist exciting opportunities within themes such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, and digital media to capitalize on this wave.
Cloud Technology Is Foundational to AI Model Adoption
There is a strong correlation between the rise of global data assets and the revenues earned by public software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies.1 As global data assets continue to grow, consumption of cloud-deployed software will likely accelerate to keep pace with that demand.2
Importantly, the worldwide growth in data assets and availability of computational power both enable progress in AI.3 Hyperscale processing facilities are set to play a critical role in facilitating the training and operation of AI systems at scale, providing AI developers with the virtually limitless resources in terms of computing and storage needed to train, test, and deploy these models. This will likely drive-up demand for not only cloud infrastructure-as-a-service, but also specialized platforms, and fast storage and networking.
Second, sophisticated models are hard to train and build. Only a select group of companies currently have the talent and data assets necessary to train and build large language models. Cloud companies are expected to play a pivotal role in the distributing artificial intelligence – building pipelines and platforms to disseminate AI models from developers to end users. Moreover, AI developers themselves are expected to be voracious consumers of cloud services, building and deploying models of the future natively on the cloud.
Third, the architectural peculiarities of the cloud model are designed for agility and nimble operation, which are critical for the split-second decisions AI powers. Running systems on public cloud platforms allows companies to harness the speed and access to data necessary to build efficient AI experiences.
Demand for AI services is expected to offer strong tailwinds to hyperscale installations and the entire value chain that feeds into the modern data centers – including storage and networking components. AI processors are expected to be a $38 billion market by 2026, up nearly 4x from 2022 levels.4 The opportunity for specialized semiconductor players is massive.
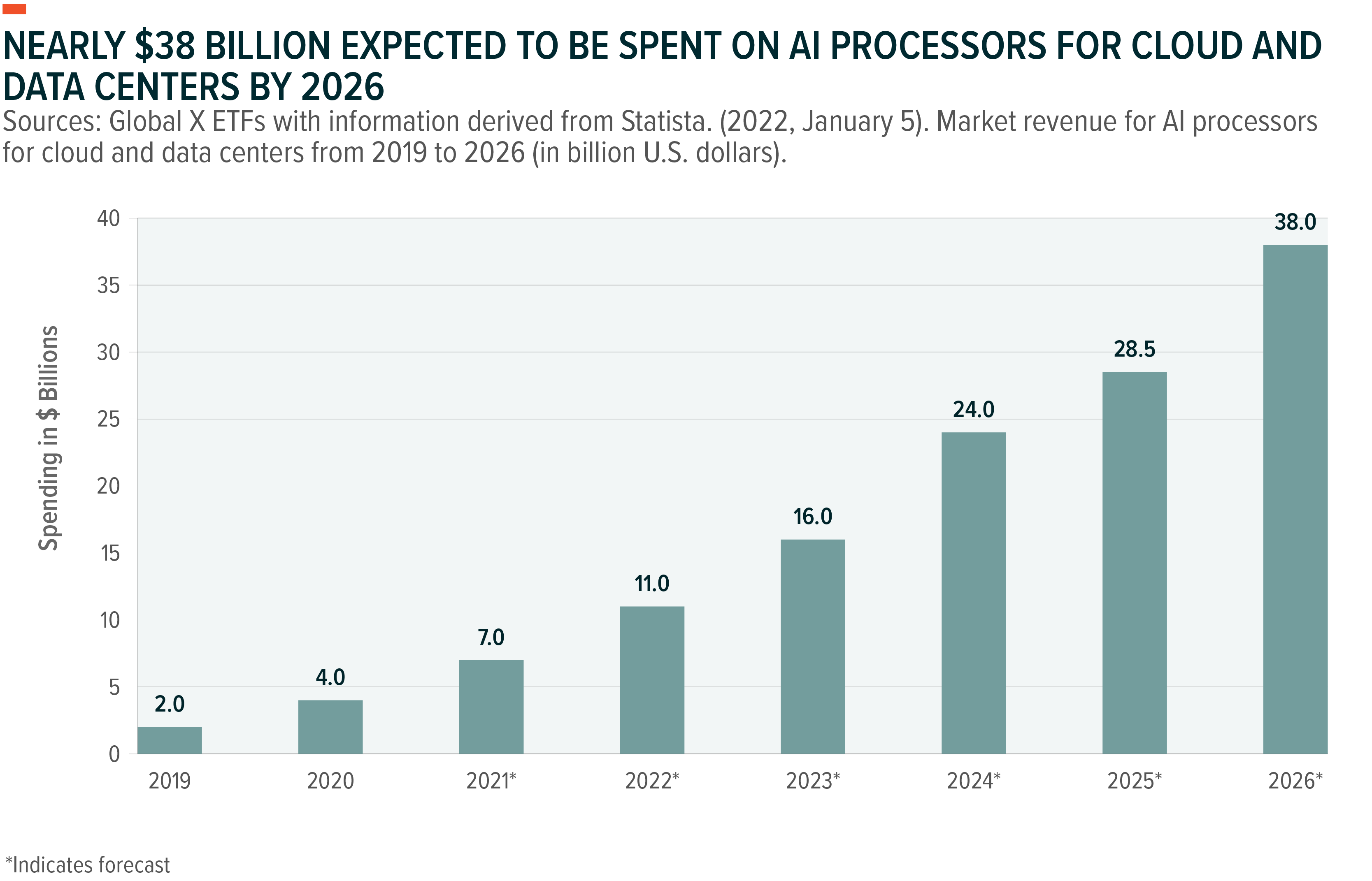
By the end of 2023, cloud infrastructure-as-a-service is anticipated to be a $150 billion market, expected to grow approximately 30% year-over-year.5 AI will accelerate this trajectory of growth. Hyperscalers, as well as the large infrastructure service providers, could leverage the AI wave to capture a new breed of consumers and cross sell more cloud products to them.
Vertical specific industry solution providers may also be in an ideal position to access valuable data and deliver differentiated add-on AI-led services. In a few notable moves, Salesforce recently announced the launch of Einstein GPT, which will allow consumers in sales and marketing divisions to access unique consumer data from the Salesforce Data Cloud and generate content that continuously adapts to growing consumer needs.6 HubSpot recently announced Chat Spot, its own model built on Chat GPT.7 Existing vendors are in a perfect position to improve tools. The opportunity to upsell is extremely attractive, and cloud software players could also improve stickiness with customers.
Lastly, the rise in AI services could boost data management apps and services. Enterprises will likely look to derive more value out of their existing data assets, pushing up the consumption of pipelining tools, databases, and more.
Overall, AI should advance the adoption of cloud computing and allow cloud infrastructure a wider total addressable market. Automated and smart software has a much bigger total addressable market (TAM) than traditional IT, as it supplements for the capabilities of the human employees using the software as well, which allows cloud providers to expand their own total addressable markets.
AI Could Help Secure the Digital Economy
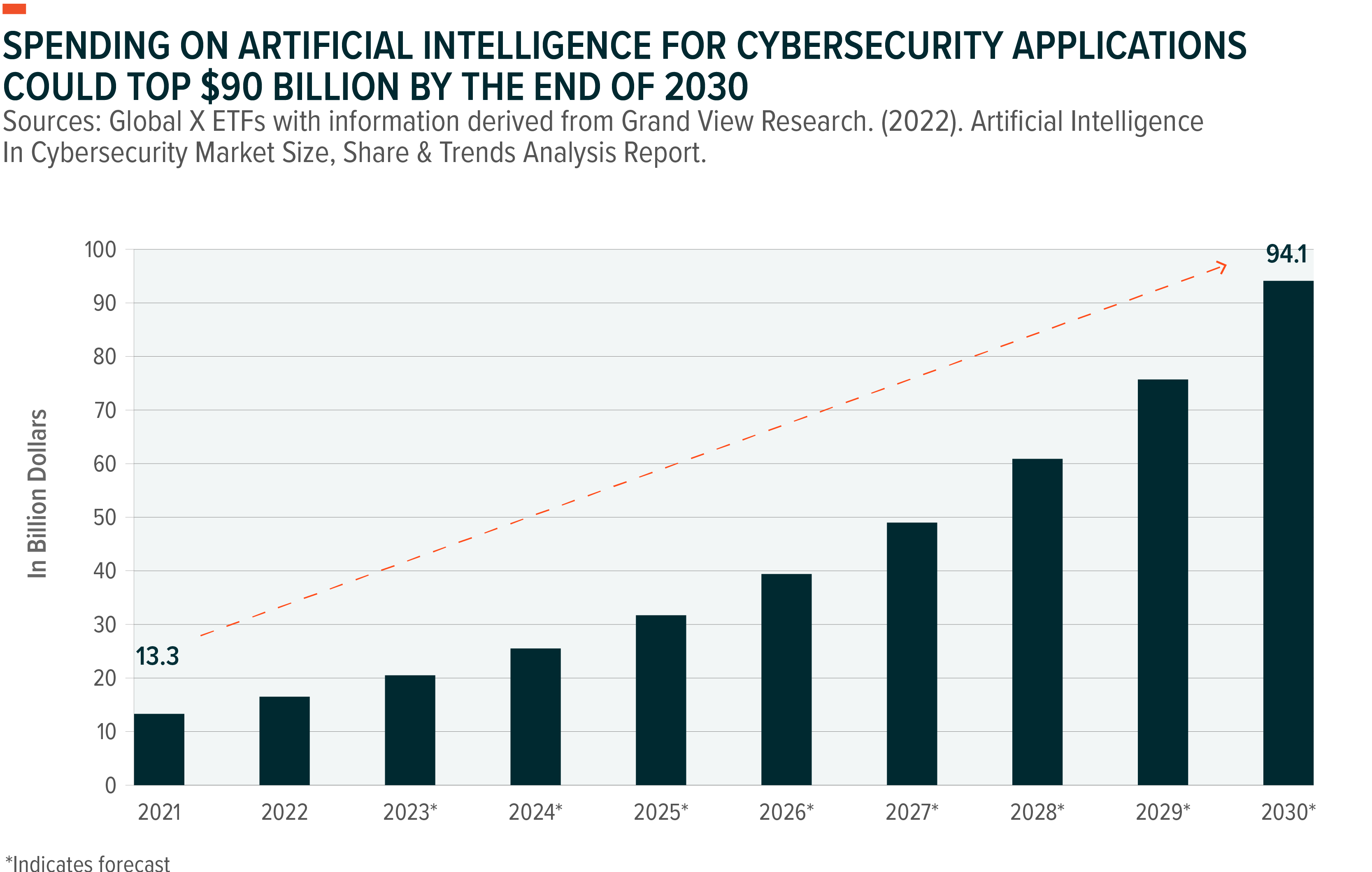
Given the vast amounts of data prevalent in cybersecurity operations, the scope for AI application is massive. Nearly $16.5 billion was spent on artificial intelligence equipped cybersecurity tools in 2022, as AI systems already play a role in cyber defenses in a limited capacity.8 Large language models could augment that.
Most of the AI systems employed today in security applications monitor data generated by large corporate IT systems for signs of breaches or malicious behavior. Human agents respond to any anomalies thereafter. Vendors such as Dynatrace, CrowdStrike, ZScaler are some of the major providers of AI and machine learning integrated offerings in the industry.9 Similarly, Google’s Gmail and Microsoft’s Outlook have been using machine learning to detect malicious emails for a while now.10
One area of impact for LLMs could be crafting automated and smart response strategies. Responding to attacks in a timely and efficient manner with the same level of intelligence as human operators could be transformative while also freeing up valuable IT resources. Moreover, generative AI models could likely be effective in formulating scenarios in which enterprise systems could be deemed vulnerable, boosting proactive defenses. This is an area where existing cloud deployed cybersecurity vendors are in an ideal position to innovate and deliver, given the data and talent they have access too.
On the other hand, generative AI is adding to cyber threats, as well. Tools like ChatGPT are being utilized to create new malware.11 Hackers are also using generative tools to craft sophisticated phishing campaigns targeting unassuming employees. In the coming months, specialized software could be developed to limit the misuse of these tools while also ensuring corporate data and assets are protected.
Lastly, AI can play a large role in eliminating talent shortages faced by the cybersecurity industry. Globally, nearly 3.5 million cybersecurity job openings are expected by 2025.12 In the US alone, nearly half a million jobs in security were vacant in 2021.13 Automated software could help boost productivity. Cyber is still a rapidly expanding field, expected to grow in spending by 13% annually through 2030.14 AI’s rise to further accelerate that spending.
Generative AI Can Transform Digital Media, Starting with Content Creation
Content creation is another function sprung into the disruptive arena with the rise of generative AI. With the help of these advanced models, creative tasks can now be automated, diversified, and customized, leading to an overall enhancement of quality. This could have massive implications for all forms of digital content creation, from social media and user generated content to digital movie or game production.
For starters, AI could play a formidable role in accelerating content creation on social media platforms. Applications targeted at marketers and content creators are rapidly gaining ground. Beyond speed of creation, automation also can reduce costs of content production. Moreover, advertisers and influencers use AI to spur creative experiments, such as identify high-engagement posts, explore new audiences, improve retention rates, and manage spending better.
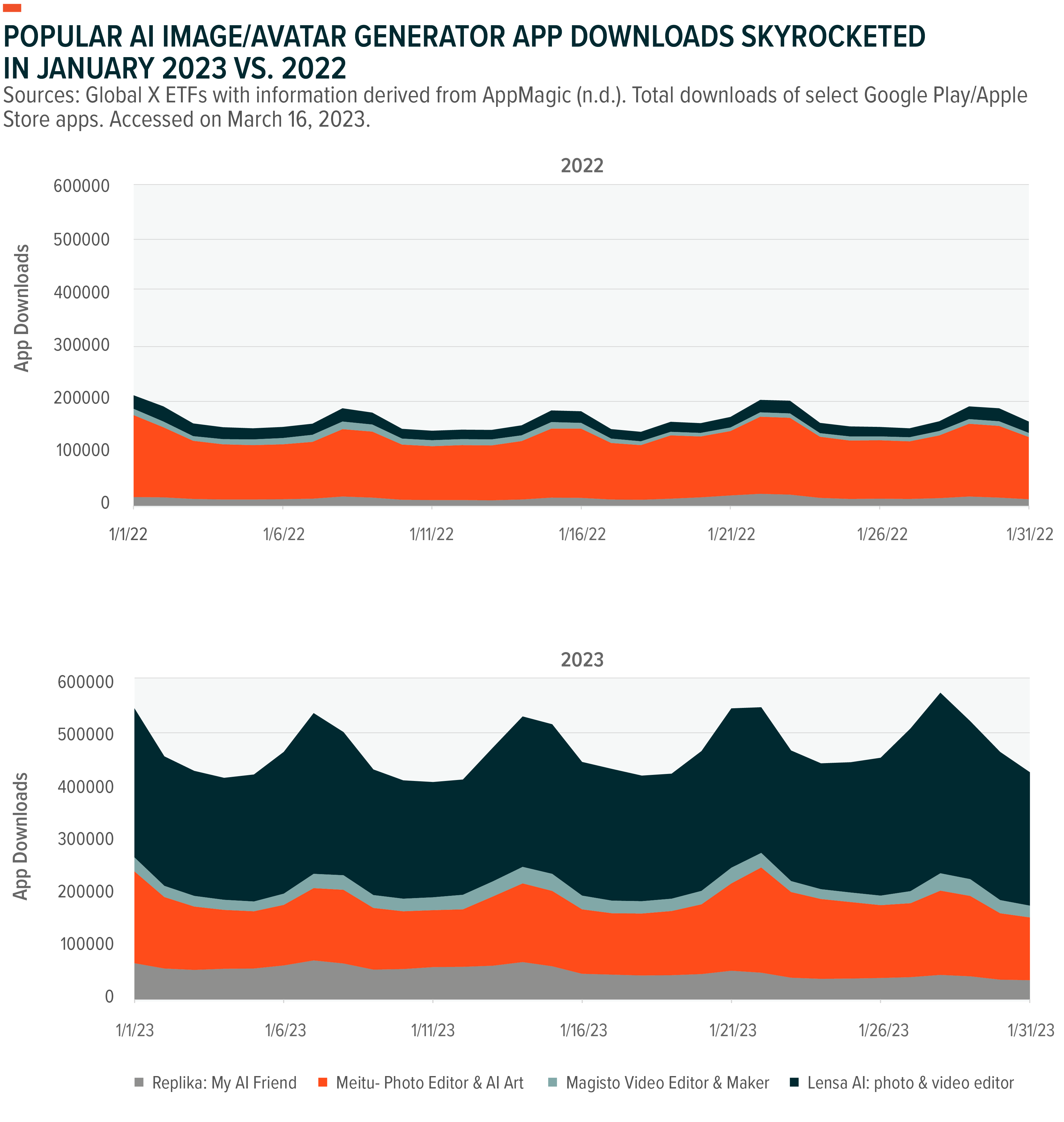
Based on an analysis of over 200 generative AI companies, nearly $320 million of generative AI funding went towards social media & marketing content between 2021 and 2022, making it one of the largest focus areas.15 Enterprises involved in visual media generation — encompassing everything from still images to lip-synced videos to avatars — have emerged as the frontrunners in generative AI deal volume. They have secured 58 deals amounting to a total of $822 million since 2021.16
In late 2022, major social media platform Meta Platforms introduced a new feature called Make-A-Video, which allows users to transform text prompts into short, high-quality video clips.17 Around the same time, Instagram experienced a viral trend where users posted portrait images generated by Lensa AI, the popular magic avatars app.18 As OpenAI’s ChatGPT-3 and Dall-E 2 tools gain popularity and AI programs become more ubiquitous, companies like Snap are embracing the trend by integrating cutting-edge tools like My AI for Snapchat+. By incorporating ChatGPT application programming interfaces (APIs), Snapchat users are provided with a highly customizable chatbot for personalized recommendations and prompts.19
These tools and functionalities allow social platforms to deepen engagement and gamify the user experience, while increasing the amount of time spent on digital platforms, ultimately monetizing users at better rates.
E-commerce, an industry closely aligned with social media as retailers continue to coalesce the two, also stands to benefit greatly from generative AI. Traditionally, AI has been used behind the scenes for fraud detection, predicting customer intent, and recommendation systems. However, the progress in AI technology means e-commerce companies can now leverage AI on the front end for virtual photoshoots, 3D product catalogs, and automated product descriptions in an effort to enhance their business performances.
Leading companies like Amazon and eBay already deploy AI services in an effort to boost their e-commerce capabilities. Aside from systems like Amazon Go, Amazon uses AI optimization to forecast consumer demand and manage inventory accordingly, while eBay offers 3D product rendering to create a natural browsing experience for buyers — as if they were in a physical store.20,21 Moreover, eBay’s low-code and no-code tools allow sellers to scan items with their phones, upload images to the eBay cloud, and convert them into 3D assets. The possibilities to boost creative productivity are endless.
Automated content creation also has massive implications for other digital media businesses. For example, in February, Netflix released ‘The Andy Warhol Diaries,’ which used generative AI voice technology to bring back Andy Warhol’s voice. In the same month, the streaming platform’s animated short ‘The Dog & The Boy’ used AI-generated images to turn storyboard landscape art into reality. Likewise, Spotify’s recent release of an AI DJ lets listeners work with the DJ to listen to music curated by someone who knows their preferences better than anyone else.
Digital services that rely on original content will likely be able to contract spending on content production in the long term as these technologies evolve and more dedicated solutions emerge, which could have a strong positive impact on their bottom lines.
Conclusion: Maximum Innovation, Maximum Impact
Artificial intelligence makes software smarter, automating mundane tasks that could result in boosted productivity and freed up resources. As adoption picks up, the broader technology space could benefit. There exist immediate opportunities that companies within cloud computing, cybersecurity, digital media, and digital commerce could leverage to accelerate disruption of legacy businesses while boosting their own top and bottom lines.
This document is not intended to be, or does not constitute, investment research